Understanding Function Calling in LLMs and Its Difference to RAG
Wells Wang • 2024/07/23
Introduction
This article explores the concept of Function Calling in Large Language Models (LLMs) and contrasts it with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). It provides a detailed explanation of both techniques, their applications, and key differences.
Function Calling in LLMs refers to the ability of a model to determine, from a user prompt, the correct function to execute from a set of available functions and the appropriate parameters to pass to that function.
Instead of generating standard text responses, LLMs for Function Calling are typically fine-tuned to return structured data responses, such as JSON objects, which can be used to execute predefined functions.
Function calling significantly expands the capabilities of LLMs by bridging the gap between natural language understanding and practical tasks, allowing models to seamlessly integrate with external systems and perform complex operations.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances LLM performance by retrieving relevant information from external data sources to inform text generation.
RAG mitigates issues such as domain knowledge gaps, factuality problems, and hallucinations by augmenting LLMs with external knowledge, making it particularly useful in knowledge-intensive scenarios.
A key advantage of RAG is that it does not require the LLM to be retrained for task-specific applications, making it ideal for applications that require continually updating knowledge.
While Function Calling allows LLMs to execute actions and interact with real-time data, RAG is best suited for building context from unstructured data that has been indexed and stored in a vector database.
Both Function Calling and RAG aim to supplement the prompt with context, whether from existing data sources or real-time APIs, to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses.
Function Calling in LLMs
Function Calling in large language models (LLMs) allows these models to extend their functionality by interfacing with external APIs and tools. This capability enables LLMs to break free from their text-based limitations and interact with the real world, performing actions, controlling devices, and retrieving information from databases.
By providing the LLM with a set of functions, along with their descriptions and usage instructions, the model can intelligently select the appropriate functions to accomplish a given task. This process is known as Function Calling, or sometimes tool use or API calling.
Function calling allows LLMs to generate structured outputs, such as JSON objects or programming language instructions, which can be reliably read by other processes. This structured output is crucial for integrating LLMs into data pipelines and ensuring that the generated data can be used for downstream processing.
The ability to define custom functions that a model can use to extend its functionality and knowledge is a significant advantage of Function Calling. These functions can supply data and abilities that LLMs typically don't have, such as real-time data, personal information, business informatics, and the ability to act upon data and update information stored elsewhere.
Function calling has emerged as a significant technique, particularly in models like OpenAI's GPT models, in how these models interact with users and the external world. It offers a structured approach to handling complex queries and tasks, bridging the gap between natural language understanding and practical tasks.
How Function Calling Works
Agent typically invoke the LLM with function-calling capabilities twice: once to map the prompt into the target function name and its input arguments, and again to send the output of the invoked function to generate the final response. This two-step process ensures that the model can accurately and efficiently perform the required tasks.

The process begins when a user submits a prompt to an application responsible for handling communication between the user and the model. This application also provides the model with one or more tool or function definitions. The model then selects the appropriate function to execute based on the user prompt.
Once the model identifies the suitable function, it returns the function name and the necessary values to the application. The application then executes the function and returns the invocation result to the model. The model uses this response to generate the final output, which is then delivered back to the user through the application.
For example, a query like What is the weather like in San Francisco? can be converted into a function call such as get_current_weather('San Francisco', 'fahrenheit').
This technique is particularly useful for creating conversational agents that can efficiently use external tools to answer complex questions. It also allows for the extraction and tagging of data, solving complex mathematical problems, and integrating with external APIs to fetch data or perform actions based on user input.
The versatility of Function Calling is evident in its ability to handle multiple, parallel, and complex function executions. This is crucial for developing AI agents that can operate across different software ecosystems and handle tasks requiring simultaneous actions.
Applications of Function Calling
Function calling has revolutionized the development of conversational agents. By enabling these models to interface with external APIs, developers can create chatbots that provide more relevant and useful responses. For instance, a chatbot can answer complex questions by calling external knowledge bases or APIs, such as retrieving the current weather in a specific location.
Another significant application of Function Calling is in natural language understanding. LLMs can convert natural language into structured JSON data, extract structured data from text, and perform tasks like Named entity recognition, Sentiment analysis, and Keyword extraction. This capability enhances the model's ability to process and understand human language in a more structured and actionable manner.
Function calling also plays a crucial role in solving complex mathematical problems. By defining custom functions, LLMs can handle advanced calculations that require multiple steps. This application is particularly useful in fields that demand precise and complex mathematical computations, such as finance and engineering.
API integration is another area where Function Calling proves invaluable. LLMs can be integrated with external APIs to fetch data or perform actions based on user input. This integration is essential for building QA systems or creative assistants that convert natural language into valid API calls, thereby enhancing the functionality and interactivity of AI applications.
Moreover, Function calling enables the development of multi-LLM applications, where different models can be chained together to create sophisticated systems. These systems, known as agents, can independently search the web, gather new data, and call other LLMs with the updated information. This chaining capability allows for the creation of highly autonomous and efficient AI systems.
What is RAG and How it works
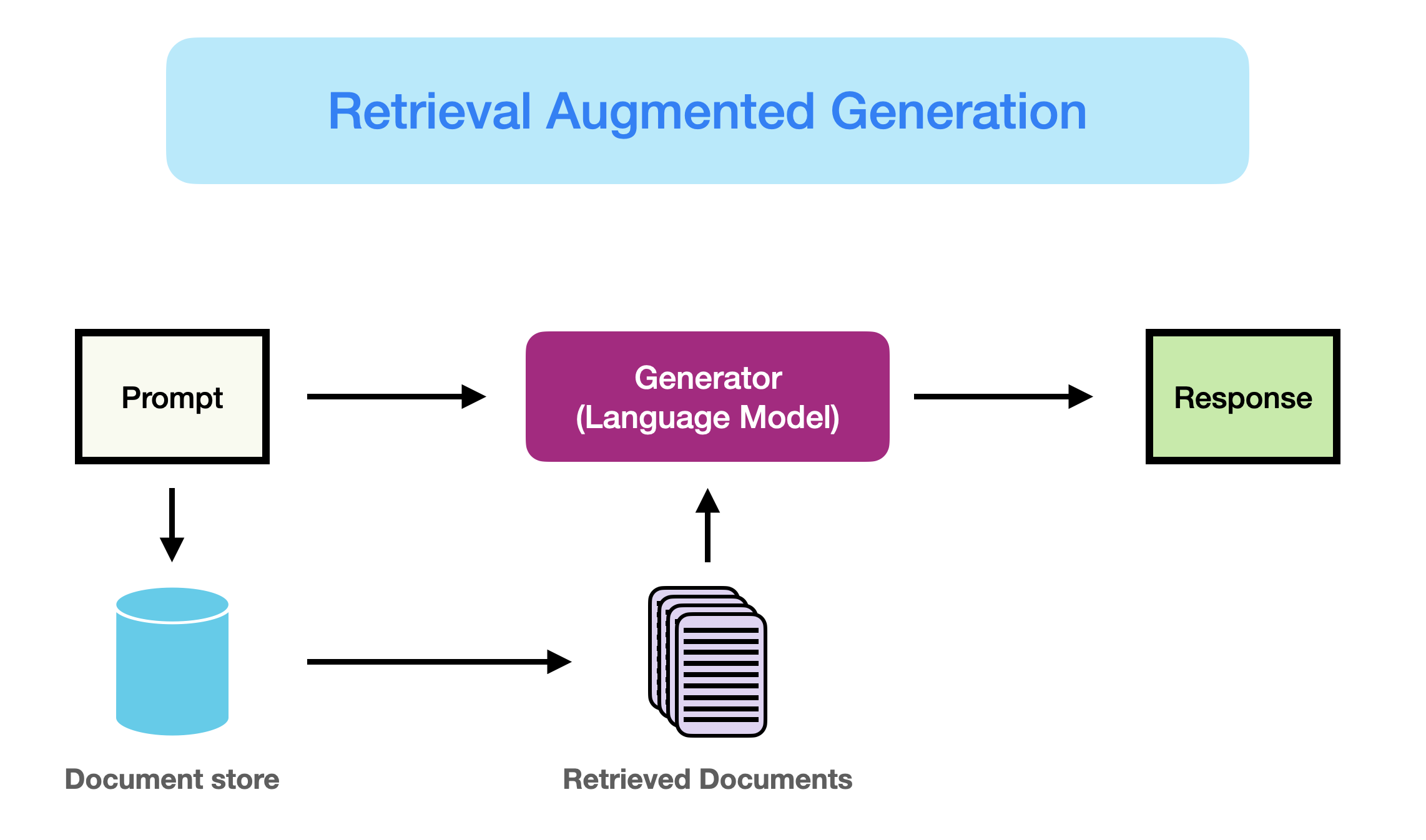
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an approach designed to enhance the performance of large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge sources into the generation process. This technique addresses key limitations of LLMs, such as outdated training data and hallucinations, by retrieving relevant, up-to-date information from authoritative databases
RAG operates by taking user input and querying a set of relevant documents from a predefined source, such as Wikipedia. These documents are then concatenated with the original input prompt and fed into the text generator, which produces the final output. This process allows RAG to provide contextually relevant responses, even in rapidly evolving domains where the LLM's static knowledge might fall short.
RAG is particularly beneficial in knowledge-intensive scenarios or domain-specific applications where information is continually updated. For instance, in conversational agents, RAG can dynamically pull the latest information, ensuring that the responses are not only relevant but also factually correct, thereby enhancing user trust and engagement.
 From www.promptingguide.ai (opens in a new tab)
From www.promptingguide.ai (opens in a new tab)
The first step in the RAG process is indexing. This involves breaking down a collection of documents into smaller chunks and generating embeddings for each chunk. These embeddings are then stored in a vector database. During inference, the user query is also converted into an embedding, which is used to search the vector database for relevant documents.
Once the relevant documents are retrieved, they are combined with the original user prompt to form a contextually enriched input. This enriched input is then fed into the LLM, which generates a response based on both the original prompt and the retrieved information. This process ensures that the generated response is both accurate and contextually relevant.
In summary, RAG enhances LLM performance by integrating external information retrieval processes. The steps of indexing, retrieval, and generation work together to provide contextually relevant responses, making RAG a powerful method for applications that require up-to-date and accurate information.
Key Differences
The primary methodological difference between Function Calling and RAG lies in their approach to enhancing LLM capabilities. Function calling relies on predefined functions to perform specific tasks, thereby enhancing their capabilities beyond text generation. While RAG focuses on retrieving and integrating external knowledge to inform text generation.
The primary methodological difference between Function Calling and RAG lies in their approach to enhancing LLM capabilities. Function calling relies on predefined functions to perform specific tasks, thereby enhancing their capabilities beyond text generation. RAG focuses on retrieving and integrating external knowledge to inform text generation.
| Feature | Function Calling | Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Uses predefined functions for task execution | Retrieves external knowledge to inform responses |
| Task Execution | Precise, structured, and real-time | Contextually enriched and accurate |
| Best Use Cases | Data retrieval, real-time information processing, interaction with external APIs | Enhancing responses with up-to-date information from large datasets |
| Example Applications | Chatbots, complex mathematical problem solving, API integration | Customer support systems, knowledge-based applications |
When to Use Each
Choosing between Function Calling and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) depends on the specific needs and scenarios of your application.
Function calling is ideal when you need to extend the capabilities of your LLM by interfacing with external APIs and tools, which can be particularly useful in applications requiring dynamic interactions with external systems.
RAG is best suited for scenarios where the primary goal is to enhance the LLM's responses by retrieving relevant information
from a large corpus of indexed data. This technique is particularly effective in reducing hallucinations and ensuring that the
model's outputs are grounded in up-to-date and accurate information. RAG is beneficial in applications where the context is
built from unstructured data, such as customer support systems or knowledge-based applications.
Function calling is advantageous in environments where quick decision-making is crucial. This method ensures that the responses are not only relevant but also precisely tailored to the needs of the application, thereby streamlining workflows and reducing the need for manual intervention.
In summary, if your application demands real-time data processing and interaction with external systems, Function Calling is the way to go. Conversely, if your application needs to enhance response accuracy by retrieving relevant information from a vast corpus, RAG is the more suitable option.
Future Trends
The future of Function Calling in LLMs is poised to revolutionize AI by enabling models to interact seamlessly with external tools and APIs, allowing LLMs to execute specific functions to extend their utility beyond text generation.
One emerging trend is the integration of Function Calling with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of both techniques, allowing LLMs to retrieve relevant information from external knowledge bases and execute specific functions for efficient task completion.
Function calling is also expected to enhance the autonomy of AI agents. By enabling LLMs to chain multiple functions and interact with various APIs, developers can create sophisticated systems capable of performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention. These Autonomous agents can independently search the web, gather new data, and execute functions, thereby streamlining workflows and reducing the need for manual input.
As the adoption of Function Calling and RAG continues to grow, there will be a greater emphasis on developing production-ready systems. This involves ensuring performance, efficiency, Data security, and Privacy, which are critical for deploying these technologies in real-world applications.